Research - Voglmeir Liu Group
Main menu:
Nutritional Glycoscience
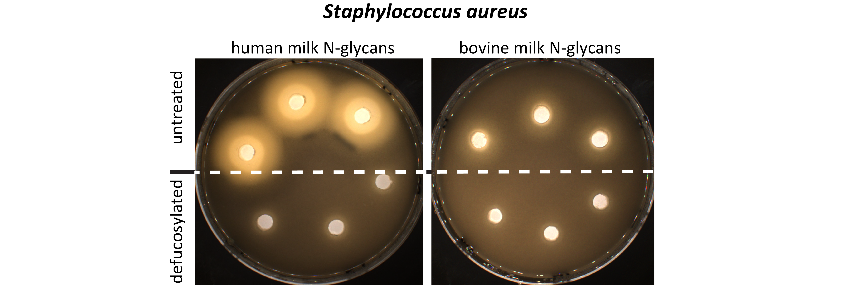
The oligosaccharides (OS) in milk are known to play essential roles in the development of the infant. However, the carbohydrate composition of milk from different animal sources as well as human milk varies. Formulated infant milkpowder made from cow milk lacks certain bioactive carbohydrate structures and shows limited amounts of N-acetylneuraminic acid and fucose, compared to human milk. Our strategy to discover the difference of bioactive carbohydrate structures in milk and the potential for the development of novel functional dairy products is based on the analysis of glycosylation profiles of free and protein bound OS with a unique chromatography-based methodology. This approach is currently also adopted for a broader range of foodstuff, which shows carbohydrate related biological functions. Additionally, the level of nutritional components (e.g. lipids) has been found to influence many biological events. The effect of the nutritional level on glycan structures is also of great interest and to monitor the structural changes, and to reveal the underlying biochemical mechanisms is another target of our research.
Recent Examples in:
Zheng et al (2019): N-Glycosylation Plays An Essential and Species-Specific Role in Anti-Infection Function of Milk Proteins Using Listeria monocytogenes as the Model Pathogen. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry 67(38): 10774-10781
Shi et al (2019): N-glycan profile as a tool in qualitative and quantitative analysis of meat adulteration. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry 67(37): 10543-10551
Wang et al (2017): Comparison of the Bifidogenic Activity of Human and Bovine Milk N-glycome. Journal of Functional Foods 33, 40-51
Wang et al (2017): Comparison of Anti-Pathogenic Activities of the Human and Bovine Milk N-Glycome: Fucosylation is a Key Factor. Food Chemistry 235: 167-174
Novel Glycoenzymes for Research and Industry
Despite the extensive usage of glycoenzymes in food and beverage industries for carbohydrate degradation, the application of currently existing glycoenzymes in analytical sciences and pharmaceutical industry has been hindered due to their limited substrate specificities. Our persuit of finding novel glycoenzymes which bear distinct functionalities is based on combining metagenomics with tedious analytical screening of substrate specificities.
Recent Examples in:
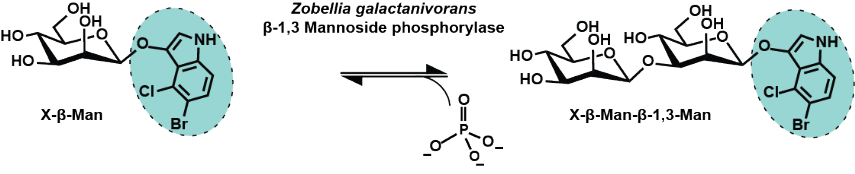
Awad et al. (2017): Discovery and biochemical characterization of a mannose phosphorylase catalyzing the synthesis of novel β-1,3-mannosides. BBA General Subjects 1861: 3221-7
Conway et al (2017): The Shewanella woodyi galactokinase pool phosphorylates glucose at the 6-position. Carbohydrate Research 455: 39-44
Awad et al (2016) Enzymatic Glycosylation of Indoxyglycosides Catalyzed by a Novel Maltose Phosphorylase from Emticicia oligotrophica. Journal of Carbohydrate Chemistry 35: 301-314
Recent Examples in:
Laborda et al (2020): An Enzymatic N‐Acylation Step Enables the Biocatalytic Synthesis of Unnatural Sialosides. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 59, 5308 –5312
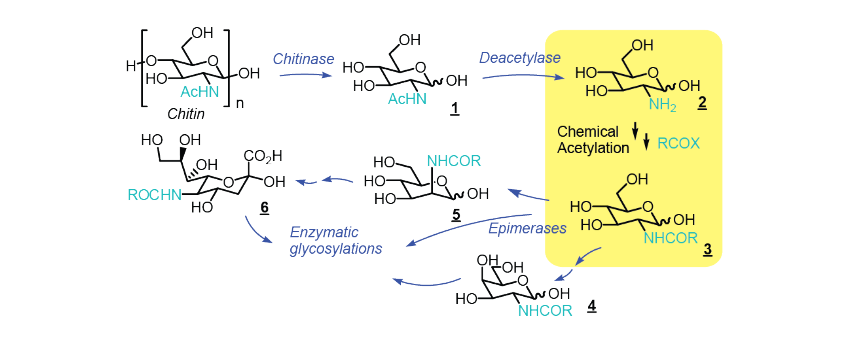
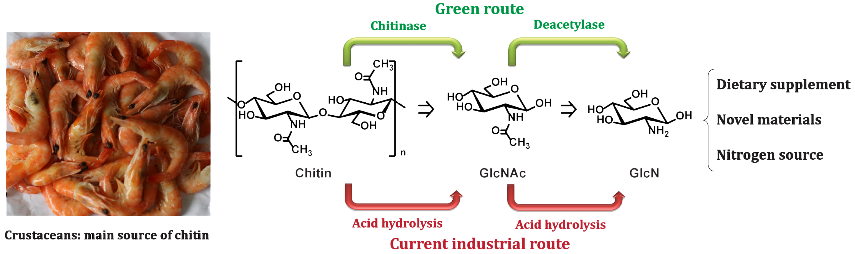
Lv et al (2017): Highly efficient and selective biocatalytic production of glucosamine from chitin. Green Chemistry 19, 527-535
Wang et al (2017). Chemo-enzymatic approach to access diastereopure α-substituted GlcNAc derivatives. Journal of Carbohydrate Chemistry 35, 423-434
Novel Glycan Labeling Technologies - Switch On Fluorescence Tags
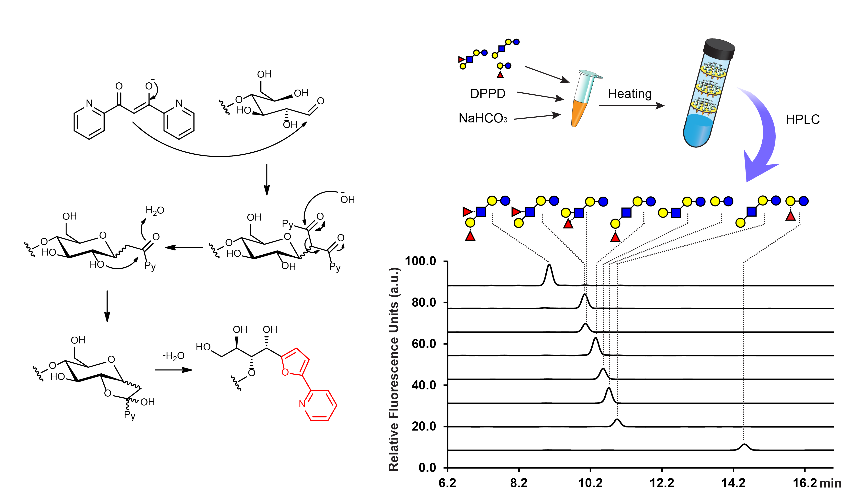
Currently we investigate applications of our proprietary reducing end labelling method ('Switch on' Derivatization). This technology allows the formation of fluorogenic substrates after derivatisation.
Examples in:
Zhang (2019): 1-(2-Aminoethyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetrafluoroborate: synthesis and application in carbohydrate analysis. Pure and Applied Chemistry 91 (9): 1441–1450
Cai et al (2017): 1,3-Di(2-dipyridyl)propan-1,3-dione – a new fluorogenic labeling reagent for milk oligosaccharides. Pure and Applied Chemistry 89 (7), 921-930
Cai et al (2014): 2-Pyridylfuran: A New Fluorescent Tag for the Analysis of Carbohydrates. Analytical Chemistry 86, 5179-86

Examples in:
Wang et al (2016): An integrated 3D-printed platform for the automated isolation of N-glycans. Carbohydrate Research 433: 14-17
Technical Service and Research Collaboration
We provide technical services for glycan structure analysis and other related tasks. Collaborations on glycoscience research are welcome.


